When you body goes into rest mode every
night, your bladder switches gears and produces less, but more
concentrated urine to let you sleep without interruption. This balance
can be cut short by a variety of factors, including disease. And while
the majority of people need a nighttime detour to the bathroom because
of the glass of wine they had in the evening and have nothing to worry
about, frequent and multiple nighttime urination is a red flag.
Even so, nocturia (the scientific term for frequent nighttime urination)
may be caused by a disease, there are some benign causes, among which
are the following:
Diuretic medications
Caffeine
Alcohol
Excessive fluids before bedtime.
As a symptom, nocturia can point to a variety of diseases, from urinary
infections to neurological diseases and everything in-between. Scroll
down to read about each cause.
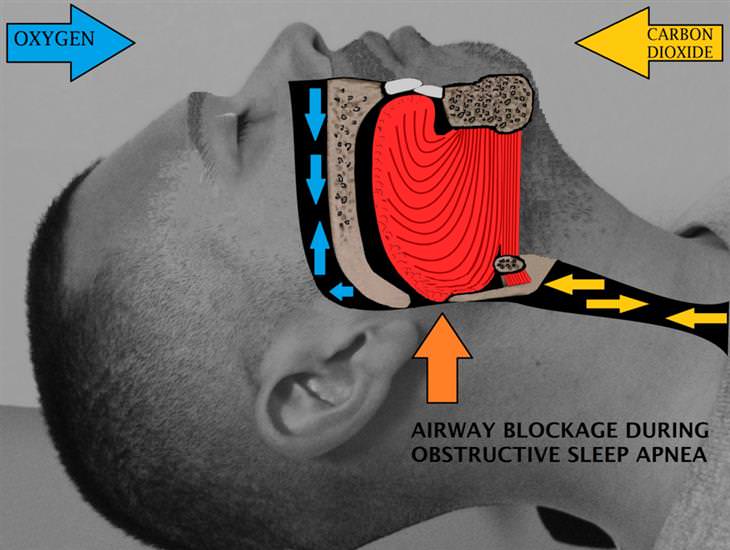
1. Obstructive Sleep Apnea

sleep apnea that it became a tell-tale sign of the disease, as
significant as snoring, but many people don’t suspect that sleep apnea
may be the cause of frequent nighttime urination. The American Sleep
Apnea Association mentions that over 84% of patients suffering from
sleep apnea reported nocturia.
report 6 or more nighttime bathroom trips. The underlying mechanism of
nocturia in sleep apnea is unclear, but it is known that patients who
start a treatment targeting sleep apnea find that it resolves the
nightly bathroom breaks almost completely.
2. Bladder Prolapse
woman’s bladder is poorly supported by pelvic muscles and ligaments, as a
result, it descends to the vaginal wall. Patients with even a minor
prolapse complain about nocturia, and bladder prolapse is one of the
leading causes of nocturia in women.
In this condition, nighttime urination
likely occurs because the tension of the vagina can aggravate the
bladder when in a horizontal position, and one gets the urge to urinate,
even when the bladder isn’t full.
3. Enlarged Prostate

prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in medical terms. In patients suffering from
BPH, the urinary tract changes its shape and functionality together
with the enlargement of the prostate.
BPH is one of the major causes of nocturia
in males, which is brought about by increased bladder sensation and the
narrowing of the urethra, which can make you feel an urgency to urinate,
even when your bladder is nearly empty. In these cases, nocturia is not
the only symptom and an increased need to urinate and incontinence are
also observed.
4. Anxiety and Depression
Mental problems, such as anxiety and
depression may manifest themselves in the form of nocturia, too.
Although the exact link between these 2 conditions is unknown, nocturia
is believed to be a side effect of sleep disturbances that come with
anxiety and depression.
the bladder that wakes a person up, but they take a trip to the bathroom
when they’re already up. To stop both the nocturia and the sleep
disturbances, it is recommended to try to relax before sleep, either by
doing breathing exercises, aromatherapy, or meditation
It is also a good idea to avoid evening naps, nighttime meals and caffeinated drinks in the evenings.
5. UTIs
One of the most common causes of nocturia
are a urinary tract infections (UTIs), cystitis, as well as bladder or
kidney infections. These infections of the urinary system usually cause
frequent burning sensations before, during and after urination, as well
as the urgency to urinate during the day and night.
in the lover back and lower pelvis.
6. Swelling of the legs ( edema)

There are many causes of edema, ranging
from liver failure to heart disease, but all of these conditions cause
excess water buildup in the tissues of the extremities.
This extra fluid has to go somewhere, so
the body transports this fluid to the kidneys to excrete it from the
body, which usually happens at night. This way, patients suffering from
leg swelling may have to take a few night trips to the bathroom.
7. Multiple Sclerosis
People who suffer from multiple sclerosis,
too, can experience nocturia, with an estimated 80 percent having some
sort of bladder dysfunction during the progression of the disease, with
some patients having to wake up 5-8 time during the night, feeling the
urge to urinate.
have suffered damage to the nervous system, which may result in the
disruption of nerve signals connected to the functioning of the bladder.
8. Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the 2nd most
common neurodegenerative disease. In the course of the disease, patient
most commonly experience motor control difficulties, but as much as 60%
of PD patients also have bladder symptoms.
Although the causes of nocturia in PD are
poorly understood, it was suggested that it may be due to higher
quantities of urine production or a lower capacity of the bladder.
9. Overactive Bladder
An overactive bladder is a diagnosis
encompassing a variety of conditions that all have the same symptom: a
sudden unstoppable urge to urinate. Nocturia is one of the symptoms of
an overactive bladder, and it is more common in people over the age of
60, but it has also been reported that one in three adults over the age
of 30 needs 2 or more nighttime bathroom trips as well.
urge to urinate, frequent incontinence, and more than 8 bathroom breaks
in a 24-hour period. The reasons of this conditions are unknown, and
therapy includes a variety of exercise, dietary restrictions, botox
injections and even electro-stimulation.
10. Tumours in Pelvic Area
Both malignant and benign tumors of the
organs of the lower abdomen, such as kidneys, reproductive organs and
the digestive system may cause nighttime urination, as the tumor may
press against the bladder, making it smaller and capable of holding less
urine.
frequent urination during the day time.
11. Diabetes
Having high blood glucose levels can make
the body get rid of excess glucose through urine. The more sugar the
urine contains, the more it stimulates urine production.
This will make you urinate more often throughout the day and night, and
it will also bring about the sensation of thirst. There is also a form
of diabetes called diabetes insipidus that causes excess urination, with
some patients urinating 20 liters (5.28 gallons) more than a normal
person every day.