Tired of feeling bloated after every meal? Constantly getting sick? Your gut might be inflamed, and it’s dragging your immune system down with it.
First, you should know that your gut controls about 70% of your immune system. When chronic inflammation takes over, your digestive system can’t do its job properly. You end up with digestive issues, low energy, mood swings, and you catch every bug that comes your way.
The good news? You can fix this with the right foods. Anti-inflammatory foods for gut health work by calming inflammation, healing your gut lining, and feeding the beneficial bacteria that keep your immune system strong.
These aren’t exotic superfoods you need to hunt down at specialty stores. Most of them are probably already in your grocery store, maybe even in your kitchen right now. When you start eating more of these foods regularly, you’ll notice better digestion, more stable energy, and you’ll get sick less often.
The best part? You don’t need to completely overhaul your diet overnight. Small, consistent changes can make a huge difference in how you feel. Ready to give your gut and your immune system the support they need? Let’s get started.
12 Anti-Inflammatory Foods That Transform Your Gut Health
1. Fatty Fish

Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna are packed with omega-3 fatty acids that directly fight inflammation in your gut. These healthy fats help repair your gut lining and reduce inflammatory markers throughout your body.
Studies show people who eat omega-3-rich fish regularly have less inflammation and better gut bacteria balance. Your beneficial bacteria use these fats to produce compounds that keep inflammation under control.
How to eat more? Aim for 2-3 servings per week. Try baked salmon with lemon, sardines on crackers, or tuna salad with avocado. Canned fish works great, too! Just choose varieties packed in water or olive oil.
3. Leafy Greens

Spinach, kale, arugula, and Swiss chard are loaded with fiber, antioxidants, and compounds that feed your good gut bacteria while starving harmful ones.
The fiber in these greens acts as food for beneficial bacteria. When these bacteria digest the fiber, they produce short-chain fatty acids that heal your gut lining and support immune function.
How to eat more? Add a handful to smoothies, toss them in pasta dishes, or try simple sautéed greens with garlic. If you’re new to greens, start small and gradually increase the amount.
4. Berries

Blueberries, strawberries, raspberries, and blackberries contain powerful antioxidants called anthocyanins that reduce gut inflammation. They also provide fiber that feeds beneficial bacteria.
Research shows people who eat berries regularly have more diverse gut bacteria, which is a sign of better overall gut health. Plus, they’re naturally sweet and satisfying.
How to eat more? Frozen berries work just as well as fresh. Add them to yogurt, oatmeal, or smoothies. Eat a handful as a snack or make a simple berry sauce for pancakes.
4. Greek Yogurt

Greek yogurt with live active cultures delivers beneficial bacteria directly to your gut while providing protein that helps repair your intestinal lining.
The probiotics in yogurt help balance your gut bacteria, reducing harmful microbes and inflammation. Look for brands that clearly state “live and active cultures” on the label.
How to eat more? Choose plain varieties to avoid added sugars. Top with berries, nuts, or a drizzle of honey. Use it in smoothies or as a substitute for sour cream in recipes.
5. Garlic

Garlic contains compounds that act as prebiotics, feeding your beneficial gut bacteria. It also has natural anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties.
Studies show garlic helps reduce harmful bacteria in the gut while promoting the growth of beneficial species. It’s one of the most powerful prebiotic foods you can eat.
How to eat more? Fresh garlic is best. Add it to stir-fries, roast whole cloves with vegetables, or make garlic-infused olive oil for pasta. Even roasted garlic becomes sweet and mild.
6. Ginger

Ginger contains compounds called gingerols that reduce inflammation and help food move through your digestive system more smoothly. It’s been used for centuries to calm upset stomachs, and research backs this up.
Studies show ginger can reduce gut inflammation and may help repair damage to your intestinal lining. It’s also excellent for nausea and general digestive discomfort.
How to eat more? Make fresh ginger tea by steeping sliced ginger in hot water. Add it to stir-fries, smoothies, or try crystallized ginger as a healthy snack.
7. Turmeric

Turmeric contains curcumin, one of the most powerful anti-inflammatory compounds found in food. It helps reduce gut inflammation and may protect your intestinal barrier from damage.
For better absorption, pair turmeric with black pepper. The piperine in pepper can increase curcumin absorption by up to 2,000%.
How to eat more? Add turmeric to soups, curries, or golden milk lattes. Try roasting vegetables with turmeric and black pepper, or add a pinch to scrambled eggs.
8. Extra Virgin Olive Oil

Extra virgin olive oil contains compounds that calm inflammation and support beneficial gut bacteria. It has oleocanthal, which works similarly to anti-inflammatory medications but naturally.
People who eat more olive oil have more diverse gut bacteria and lower levels of inflammatory markers. The key is choosing high-quality, extra virgin varieties.
How to eat more? Drizzle over salads, use for light cooking, or dip bread in it. Avoid using it at very high temperatures to preserve its beneficial compounds.
9. Bone Broth

Bone broth is rich in collagen, gelatin, and amino acids that help repair and strengthen your gut lining. These compounds provide the building blocks your intestinal cells need to heal.
The gelatin in bone broth can help seal gaps in your gut lining, while amino acids like glycine and glutamine support tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
How to eat more? Sip it warm as a snack, use it as a base for soups, or cook rice and quinoa in it instead of water for extra flavor and nutrients.
10. Fermented Vegetables
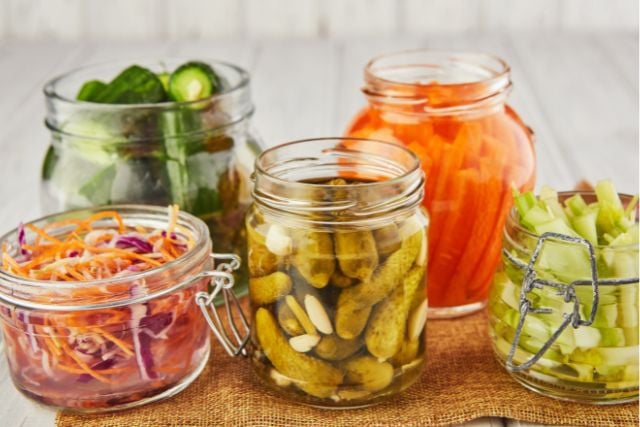

Sauerkraut, kimchi, and fermented pickles are loaded with beneficial bacteria that help balance your gut microbiome. They’re also rich in fiber that feeds these good bacteria.
Different fermented foods contain different strains of beneficial bacteria. The more variety you eat, the more diverse your gut bacteria become, which is better for your immune system.
How to eat more? Start with small amounts, about a tablespoon daily, and gradually increase. Add them to salads, sandwiches, or eat them as a side dish with meals.
11. Avocados
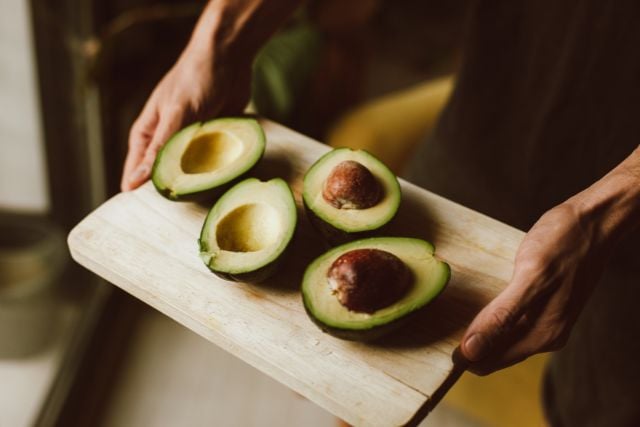

Avocados provide both fiber and monounsaturated fats that support gut health. They help feed beneficial bacteria while providing compounds that reduce inflammation throughout your body.
Research shows people who eat avocados regularly have more diverse gut bacteria and higher levels of beneficial microbes. They’re also incredibly versatile.
How to eat more? Beyond toast and guacamole, add avocado to smoothies for creaminess, use in salad dressings, or stuff with tuna or chicken salad for a quick meal.
12. Green Tea
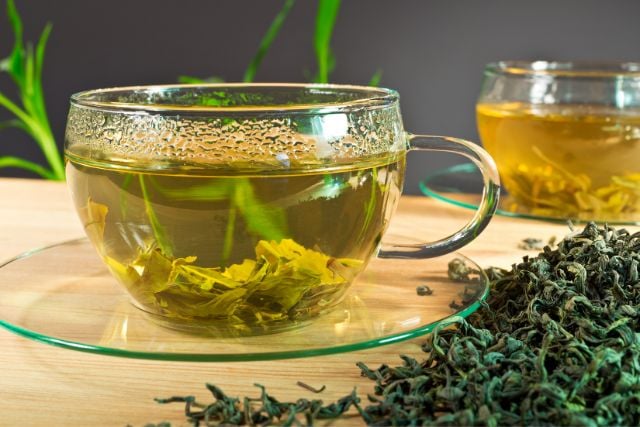

Green tea contains catechins, particularly EGCG, which have anti-inflammatory effects. Regular green tea consumption is linked to better gut bacteria balance and reduced inflammation.
The polyphenols in green tea feed beneficial bacteria while inhibiting harmful ones. It’s a simple daily habit that supports long-term gut health.
How to eat more? Aim for 2-3 cups daily. Avoid drinking it with meals since it can interfere with iron absorption. Try different varieties like sencha or matcha for variety.
Why Gut Health Determines Your Immunity
Your gut is your body’s first line of defense. When it gets inflamed, the lining becomes “leaky,” allowing harmful substances into your bloodstream. This triggers your immune system to work overtime, attacking everything it sees as a threat.
The result? You get sick more often and feel exhausted. Chronic gut inflammation is linked to frequent colds, autoimmune issues, and even heart disease.
Anti-inflammatory foods change this. They reduce inflammation, repair your gut lining, and feed beneficial bacteria that actually boost immune function. Most people notice better digestion and more energy within weeks.
Simple Ways to Add These Foods Daily

You don’t need to eat all these foods every day. Start by picking 2-3 that you already enjoy and focus on eating them more regularly. Once that becomes a habit, add more.
Try Greek yogurt with berries for breakfast, add leafy greens to your lunch, snack on a handful of nuts, and end your day with green tea. Small changes add up to big results.
Meal prep makes this easier. Wash and chop vegetables when you get home from shopping, cook a big batch of bone broth on weekends, or keep frozen berries on hand for quick smoothies.
Foods That Increase Gut Inflammation

While you’re adding healing foods, consider reducing foods that increase inflammation. Ultra-processed foods, excess sugar, refined carbs, and fried foods can disrupt your gut bacteria balance.
You don’t have to eliminate these completely, but try making them occasional treats rather than daily staples. Your gut will appreciate the break, and you’ll likely feel less bloated and more energetic.
Final Thought
Your gut health doesn’t have to be complicated. These 12 anti-inflammatory foods are already sitting in most grocery stores, waiting to transform how you feel.
Start with just one or two foods this week. Add berries to your breakfast. Swap regular tea for green tea. Cook with more garlic and ginger. Small changes create big results.
Your gut and your immune system are ready for the upgrade. All you have to do is start.










