|
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body produces or uses insulin. According to the American Diabetes Association, in the U.S, about 1.2 million people are diagnosed with diabetes each year. Estimates are that over 11% of the population has diabetes.
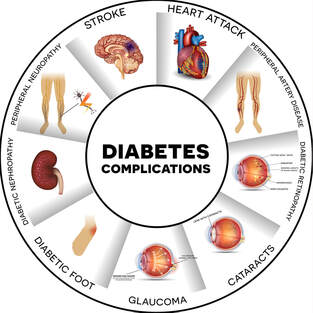
Diabetes affects your blood sugar levels, which can lead to various types of complications. One of those complications is potentially serious eye and vision problems. For example, according to the National Eye Institute, about 50% of individuals with diabetes will develop diabetic retinopathy. |
Continuing reading for an understanding of how diabetes affects your vision and eye health and what proactive steps you can take.
What is diabetic eye disease?
Diabetic retinopathy: Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage the blood vessels in the retina. The blood vessels may leak or grow abnormally. This leads to changes in vision and potentially vision loss. It is the most common eye disease related to diabetes.
Diabetic macular edema (DME): DME involves swelling of the macula, which is the central part of the retina that helps us have sharp vision
Cataracts: Cataracts involve clouding in the eye’s lens, which helps focus light into the retina. Although cataracts can also develop in people without diabetes, individuals with diabetes are two to five times more likely to develop them than those without the condition.
Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a condition that causes damage to the optic nerve and gradual loss of vision. Having diabetes increases your risk of developing glaucoma.
How does having diabetes affect the eyes?
Early signs and symptoms of diabetic eye diseases
- Blurry vision
- Floaters or dark spots
- Problems seeing at night
- Colors appearing faded
- Blank or dark areas in your field of vision
Why regular eye exams are vital
Although it may vary, the American Diabetes Association usually recommends a comprehensive eye exam yearly for individuals with diabetes; however, your doctor may suggest more frequent eye exams depending on your specific needs.
Treatment for diabetic eye diseases
- Good blood sugar control: This includes tight monitoring of your blood sugar to maintain appropriate levels, which can slow damage progression.
- Laser therapy: Laser therapy helps reduce abnormal blood vessels.
- Anti-VEGF injections: This involve injections to help prevent the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina and reduce swelling.
- Vitrectomy surgery: In advanced eye disease, surgery may be helpful to remove blood or scar tissue from the eye.
How can you protect your vision if you have diabetes?
- Keep your blood sugar in target range as directed by your doctor.
- Get regular exercise.
- Monitor and control blood pressure levels.
- Avoid smoking.
- Immediately tell your eye doctor about vision changes.
- Don’t skip regular eye exams.
Remember, diabetes doesn’t mean you will go on to develop diabetic eye diseases. With comprehensive eye exams, early detection, good blood sugar control, and healthy lifestyle choices, you can protect your vision and your overall quality of life.
If you would like to ask whether an appointment with one of our eye doctors would be appropriate at this time, call our office at 508-746-8600.